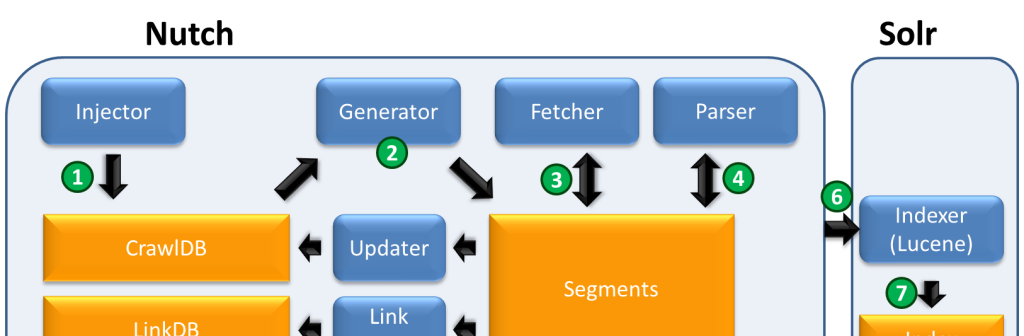
Tips de configuración
He estado haciendo este fin de semana unas pruebas de concepto para
poder usar solrCloud, en su
última versión, conjuntamente con el crawler nutch, también en su
última versión. He encontrado muchos documentos explicando cómo
configurar el sistema con solr normal pero no para usarlos con solrCloud.
Voy a describir, someramente, un conjuntode tips que
he aprendido este fin de semana mientras he realizado la prueba de concepto.
Lo primero que hay que tener instalado y configurado es
- Nutch 1.13, para ello basta con seguir este documento
- SolrCloud 6.6.0, para ello basta con seguir este documento
Una vez que tenemos una web recolectada con nutch (siguiendo el
manual indicado es una tarea sencilla), el problema es pasarla a solr.
Para ello, en teoría solo hay que ejecutar el siguiente comando
bin/nutch index crawl/crawldb -linkdb crawl/linkdb crawl/segments/20170630203428
El problema es que para ejecutar este comando hay disponer de una
colección creada, para lo que hay que disponer de un esquema válido
para solrCloud 6.6.0
Lo primero que vamos a hacer es crear la colección sobre el cluster
de solr, para lo que vamos a ejecutar el siguiente comando
./bin/solr create -c nutch_collection -d ./server/solr/nutchconfig/conf -n nucth_config -shards 2 -replicationFactor 2
Para poder ejecutar el comando tenemos que haber copiado un esquema
en la carpeta server/solr/nutchconfig. Copiar un
esquema consiste en, copiar uno existente y modificarlo
- Copiar una configuración básica de las existentes
solr-6.6.0/server/solr/configsets/basic_configs a solr-6.6.0/server/solr/nutchconfig - Copiar el schema.xml de nutch a la nueva
configuración
solr-6.6.0/server/solr/nutchconfig/managed-schema y
adaptarlo a la nueva notación solr-6.6.0/server/solr/nutchconfig/managed-schema
El schema adaptado queda algo similar a lo siguiente
<schema name="nutch" version="1.6">
<types>
<!-- The StrField type is not analyzed, but indexed/stored verbatim. -->
<fieldType name="string" class="solr.StrField" sortMissingLast="true" omitNorms="true"/>
<fieldtype name="binary" class="solr.BinaryField"/>
<!--
Default numeric field types. For faster range queries, consider the tint/tfloat/tlong/tdouble types.
-->
<fieldType name="int" class="solr.TrieIntField" precisionStep="0" omitNorms="true" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<fieldType name="float" class="solr.TrieFloatField" precisionStep="0" omitNorms="true" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<fieldType name="long" class="solr.TrieLongField" precisionStep="0" omitNorms="true" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<fieldType name="double" class="solr.TrieDoubleField" precisionStep="0" omitNorms="true" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<!--
Numeric field types that index each value at various levels of precision
to accelerate range queries when the number of values between the range
endpoints is large. See the javadoc for NumericRangeQuery for internal
implementation details.
Smaller precisionStep values (specified in bits) will lead to more tokens
indexed per value, slightly larger index size, and faster range queries.
A precisionStep of 0 disables indexing at different precision levels.
-->
<fieldType name="tint" class="solr.TrieIntField" precisionStep="8" omitNorms="true" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<fieldType name="tfloat" class="solr.TrieFloatField" precisionStep="8" omitNorms="true" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<fieldType name="tlong" class="solr.TrieLongField" precisionStep="8" omitNorms="true" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<fieldType name="tdouble" class="solr.TrieDoubleField" precisionStep="8" omitNorms="true" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<fieldType name="pdates" class="solr.DatePointField" docValues="true" multiValued="true"/>
<fieldType name="tints" class="solr.TrieIntField" docValues="true" precisionStep="8" positionIncrementGap="0" multiValued="true"/>
<fieldType name="tfloats" class="solr.TrieFloatField" docValues="true" precisionStep="8" positionIncrementGap="0" multiValued="true"/>
<fieldType name="tlongs" class="solr.TrieLongField" docValues="true" precisionStep="8" positionIncrementGap="0" multiValued="true"/>
<fieldType name="tdoubles" class="solr.TrieDoubleField" docValues="true" precisionStep="8" positionIncrementGap="0" multiValued="true"/>
<fieldType name="dates" class="solr.TrieDateField" docValues="true" precisionStep="0" positionIncrementGap="0" multiValued="true"/>
<!-- The format for this date field is of the form 1995-12-31T23:59:59Z, and
is a more restricted form of the canonical representation of dateTime
http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-2/#dateTime
The trailing "Z" designates UTC time and is mandatory.
Optional fractional seconds are allowed: 1995-12-31T23:59:59.999Z
All other components are mandatory.
Expressions can also be used to denote calculations that should be
performed relative to "NOW" to determine the value, ie...
NOW/HOUR
... Round to the start of the current hour
NOW-1DAY
... Exactly 1 day prior to now
NOW/DAY+6MONTHS+3DAYS
... 6 months and 3 days in the future from the start of
the current day
Consult the DateField javadocs for more information.
Note: For faster range queries, consider the tdate type
-->
<fieldType name="date" class="solr.TrieDateField" omitNorms="true" precisionStep="0" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<fieldType name="location" class="solr.LatLonType" subFieldSuffix="_coordinate"/>
<!-- A Trie based date field for faster date range queries and date faceting. -->
<fieldType name="tdate" class="solr.TrieDateField" omitNorms="true" precisionStep="6" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<fieldType name="tdates" class="solr.TrieDateField" docValues="true" precisionStep="6" positionIncrementGap="0" multiValued="true"/>
<!-- solr.TextField allows the specification of custom text analyzers
specified as a tokenizer and a list of token filters. Different
analyzers may be specified for indexing and querying.
The optional positionIncrementGap puts space between multiple fields of
this type on the same document, with the purpose of preventing false phrase
matching across fields.
For more info on customizing your analyzer chain, please see
http://wiki.apache.org/solr/AnalyzersTokenizersTokenFilters
-->
<!-- A general text field that has reasonable, generic
cross-language defaults: it tokenizes with StandardTokenizer,
removes stop words from case-insensitive "stopwords.txt"
(empty by default), and down cases. At query time only, it
also applies synonyms. -->
<fieldType name="text_general" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer type="index">
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="stopwords.txt"/>
<!-- in this example, we will only use synonyms at query time
<filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="index_synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="false"/>
-->
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
<analyzer type="query">
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="stopwords.txt"/>
<filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="true"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- A text field with defaults appropriate for English: it
tokenizes with StandardTokenizer, removes English stop words
(stopwords.txt), down cases, protects words from protwords.txt, and
finally applies Porter's stemming. The query time analyzer
also applies synonyms from synonyms.txt. -->
<fieldType name="text_en" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer type="index">
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<!-- in this example, we will only use synonyms at query time
<filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="index_synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="false"/>
-->
<!-- Case insensitive stop word removal.
add enablePositionIncrements=true in both the index and query
analyzers to leave a 'gap' for more accurate phrase queries.
-->
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory"
ignoreCase="true"
words="lang/stopwords_en.txt"
/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.EnglishPossessiveFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.KeywordMarkerFilterFactory" protected="protwords.txt"/>
<!-- Optionally you may want to use this less aggressive stemmer instead of PorterStemFilterFactory:
<filter class="solr.EnglishMinimalStemFilterFactory"/>
-->
<filter class="solr.PorterStemFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
<analyzer type="query">
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="true"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory"
ignoreCase="true"
words="lang/stopwords_en.txt"
/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.EnglishPossessiveFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.KeywordMarkerFilterFactory" protected="protwords.txt"/>
<!-- Optionally you may want to use this less aggressive stemmer instead of PorterStemFilterFactory:
<filter class="solr.EnglishMinimalStemFilterFactory"/>
-->
<filter class="solr.PorterStemFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- A text field with defaults appropriate for English, plus
aggressive word-splitting and autophrase features enabled.
This field is just like text_en, except it adds
WordDelimiterFilter to enable splitting and matching of
words on case-change, alpha numeric boundaries, and
non-alphanumeric chars. This means certain compound word
cases will work, for example query "wi fi" will match
document "WiFi" or "wi-fi". However, other cases will still
not match, for example if the query is "wifi" and the
document is "wi fi" or if the query is "wi-fi" and the
document is "wifi".
-->
<fieldType name="text_en_splitting" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100" autoGeneratePhraseQueries="true">
<analyzer type="index">
<tokenizer class="solr.WhitespaceTokenizerFactory"/>
<!-- in this example, we will only use synonyms at query time
<filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="index_synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="false"/>
-->
<!-- Case insensitive stop word removal.
add enablePositionIncrements=true in both the index and query
analyzers to leave a 'gap' for more accurate phrase queries.
-->
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory"
ignoreCase="true"
words="lang/stopwords_en.txt"
/>
<filter class="solr.WordDelimiterFilterFactory" generateWordParts="1" generateNumberParts="1" catenateWords="1" catenateNumbers="1" catenateAll="0" splitOnCaseChange="1"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.KeywordMarkerFilterFactory" protected="protwords.txt"/>
<filter class="solr.PorterStemFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
<analyzer type="query">
<tokenizer class="solr.WhitespaceTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="true"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory"
ignoreCase="true"
words="lang/stopwords_en.txt"
/>
<filter class="solr.WordDelimiterFilterFactory" generateWordParts="1" generateNumberParts="1" catenateWords="0" catenateNumbers="0" catenateAll="0" splitOnCaseChange="1"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.KeywordMarkerFilterFactory" protected="protwords.txt"/>
<filter class="solr.PorterStemFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Less flexible matching, but less false matches. Probably not ideal for product names,
but may be good for SKUs. Can insert dashes in the wrong place and still match. -->
<fieldType name="text_en_splitting_tight" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100" autoGeneratePhraseQueries="true">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.WhitespaceTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="false"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_en.txt"/>
<filter class="solr.WordDelimiterFilterFactory" generateWordParts="0" generateNumberParts="0" catenateWords="1" catenateNumbers="1" catenateAll="0"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.KeywordMarkerFilterFactory" protected="protwords.txt"/>
<filter class="solr.EnglishMinimalStemFilterFactory"/>
<!-- this filter can remove any duplicate tokens that appear at the same position - sometimes
possible with WordDelimiterFilter in conjuncton with stemming. -->
<filter class="solr.RemoveDuplicatesTokenFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Just like text_general except it reverses the characters of
each token, to enable more efficient leading wildcard queries. -->
<fieldType name="text_general_rev" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer type="index">
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="stopwords.txt"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.ReversedWildcardFilterFactory" withOriginal="true"
maxPosAsterisk="3" maxPosQuestion="2" maxFractionAsterisk="0.33"/>
</analyzer>
<analyzer type="query">
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="true"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="stopwords.txt"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<fieldtype name="phonetic" stored="false" indexed="true" class="solr.TextField" >
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.DoubleMetaphoneFilterFactory" inject="false"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldtype>
<fieldtype name="payloads" stored="false" indexed="true" class="solr.TextField" >
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.WhitespaceTokenizerFactory"/>
<!--
The DelimitedPayloadTokenFilter can put payloads on tokens... for example,
a token of "foo|1.4" would be indexed as "foo" with a payload of 1.4f
Attributes of the DelimitedPayloadTokenFilterFactory :
"delimiter" - a one character delimiter. Default is | (pipe)
"encoder" - how to encode the following value into a playload
float -> org.apache.lucene.analysis.payloads.FloatEncoder,
integer -> o.a.l.a.p.IntegerEncoder
identity -> o.a.l.a.p.IdentityEncoder
Fully Qualified class name implementing PayloadEncoder, Encoder must have a no arg constructor.
-->
<filter class="solr.DelimitedPayloadTokenFilterFactory" encoder="float"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldtype>
<!-- lowercases the entire field value, keeping it as a single token. -->
<fieldType name="lowercase" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.KeywordTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory" />
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<fieldType name="url" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.WordDelimiterFilterFactory" generateWordParts="1" generateNumberParts="1"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<fieldType name="text_path" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.PathHierarchyTokenizerFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- since fields of this type are by default not stored or indexed,
any data added to them will be ignored outright. -->
<fieldtype name="ignored" stored="false" indexed="false" multiValued="true" class="solr.StrField" />
<!-- boolean type: "true" or "false" -->
<fieldType name="boolean" class="solr.BoolField" sortMissingLast="true"/>
<fieldType name="booleans" class="solr.BoolField" sortMissingLast="true" multiValued="true"/>
<!-- sortMissingLast and sortMissingFirst attributes are optional attributes are
currently supported on types that are sorted internally as strings
and on numeric types.
This includes "string","boolean", and, as of 3.5 (and 4.x),
int, float, long, date, double, including the "Trie" variants.
- If sortMissingLast="true", then a sort on this field will cause documents
without the field to come after documents with the field,
regardless of the requested sort order (asc or desc).
- If sortMissingFirst="true", then a sort on this field will cause documents
without the field to come before documents with the field,
regardless of the requested sort order.
- If sortMissingLast="false" and sortMissingFirst="false" (the default),
then default lucene sorting will be used which places docs without the
field first in an ascending sort and last in a descending sort.
-->
</types>
<fields>
<field name="id" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" required="true"/>
<field name="_version_" type="long" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<!-- core fields -->
<field name="segment" type="string" stored="true" indexed="false"/>
<field name="digest" type="string" stored="true" indexed="false"/>
<field name="boost" type="float" stored="true" indexed="false"/>
<!-- fields for index-basic plugin -->
<field name="host" type="url" stored="false" indexed="true"/>
<field name="url" type="url" stored="true" indexed="true"/>
<!-- stored=true for highlighting, use term vectors and positions for fast highlighting -->
<field name="content" type="text_general" stored="true" indexed="true"/>
<field name="title" type="text_general" stored="true" indexed="true"/>
<field name="cache" type="string" stored="true" indexed="false"/>
<field name="tstamp" type="date" stored="true" indexed="false"/>
<!-- fields for index-geoip plugin -->
<field name="ip" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="cityName" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="cityConfidence" type="int" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="cityGeoNameId" type="int" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="continentCode" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="continentGeoNameId" type="int" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="contentName" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="countryIsoCode" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true"/>
<field name="countryName" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="countryConfidence" type="int" stored="true" indexed="true"/>
<field name="countryGeoNameId" type="int" stored="true" indexed="true"/>
<field name="latLon" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true"/>
<field name="accRadius" type="int" stored="true" indexed="true"/>
<field name="timeZone" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true"/>
<field name="metroCode" type="int" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="postalCode" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="postalConfidence" type="int" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="countryType" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="subDivName" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="subDivIsoCode" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="subDivConfidence" type="int" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="subDivGeoNameId" type="int" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="autonSystemNum" type="int" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="autonSystemOrg" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="domain" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="isp" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="org" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="userType" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="isAnonProxy" type="boolean" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="isSatelitteProv" type="boolean" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="connType" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<field name="location" type="location" stored="true" indexed="true" />
<dynamicField name="*_coordinate" type="tdouble" indexed="true" stored="false"/>
<!-- catch-all field -->
<field name="text" type="text_general" stored="false" indexed="true" multiValued="true"/>
<!-- fields for index-anchor plugin -->
<field name="anchor" type="text_general" stored="true" indexed="true"
multiValued="true"/>
<!-- fields for index-more plugin -->
<field name="type" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" multiValued="true"/>
<field name="contentLength" type="string" stored="true" indexed="false"/>
<field name="lastModified" type="date" stored="true" indexed="false"/>
<field name="date" type="tdate" stored="true" indexed="true"/>
<!-- fields for languageidentifier plugin -->
<field name="lang" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true"/>
<!-- fields for subcollection plugin -->
<field name="subcollection" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" multiValued="true"/>
<!-- fields for feed plugin (tag is also used by microformats-reltag)-->
<field name="author" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true"/>
<field name="tag" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" multiValued="true"/>
<field name="feed" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true"/>
<field name="publishedDate" type="date" stored="true" indexed="true"/>
<field name="updatedDate" type="date" stored="true" indexed="true"/>
<!-- fields for creativecommons plugin -->
<field name="cc" type="string" stored="true" indexed="true" multiValued="true"/>
<!-- fields for tld plugin -->
<field name="tld" type="string" stored="false" indexed="false"/>
<!-- field containing segment's raw binary content if indexed with -addBinaryContent -->
<field name="binaryContent" type="binary" stored="true" indexed="false"/>
</fields>
<uniqueKey>id</uniqueKey>
<!--<defaultSearchField>text</defaultSearchField>-->
<!--<solrQueryParser defaultOperator="OR"/>-->
<!-- copyField commands copy one field to another at the time a document
is added to the index. It's used either to index the same field differently,
or to add multiple fields to the same field for easier/faster searching. -->
<copyField source="content" dest="text"/>
<copyField source="url" dest="text"/>
<copyField source="title" dest="text"/>
<copyField source="anchor" dest="text"/>
<copyField source="author" dest="text"/>
<copyField source="latLon" dest="location"/>
</schema>
En este momento deberíamos tener ya la colección
nutch_collection en solrCloud creada, y lista para su uso

Y deberíamos tener la configuración accesible dede al interfaz web de solr
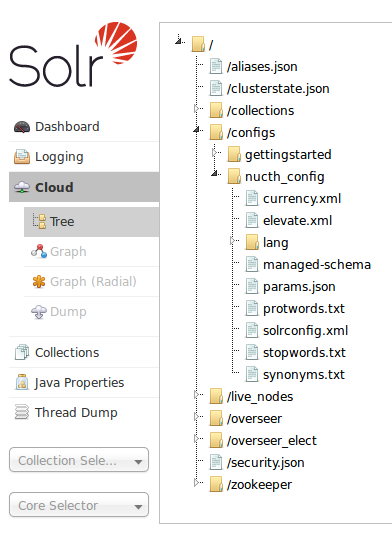
Si has seguido el quickstart de solr para su instalación deberías ver
dos colecciones y dos configuraciones. La que se crea de prueba y la
creada con el comando para nutch
Ahora, en teoría ya solo quedaría mandar los resultados de la
recolección al índice/collection creado. Para ello basta con ejecutar
el siguiente comando
bin/nutch index crawl/crawldb -linkdb crawl/linkdb crawl/segments/20170630203428
Si lo ejecutas sin más dará errores, ya que nos falta configurar el
plugin de solr en nutch, para ello hay que hacer los siguientes
cambios en el fichero nutch-site.xml
Cambiar el valor de plugin.includes
protocol-http|urlfilter-regex|parse-(html|tika)|index-(basic|anchor)|indexer-elastic|scoring-opic|urlnormalizer-(pass|regex|basic)
por
protocol-http|urlfilter-regex|parse-(html|tika)|index-(basic|anchor)|indexer-solr|scoring-opic|urlnormalizer-(pass|regex|basic)
Cambiar el valor de solr.server.type
http
por
cloud
Cambiar el valor de solr.server.url
http://127.0.0.1:8983/solr/
por
http://127.0.0.1:8983/solr/nutch_collection/
Cambiar el valor de solr.zookeeper.url
por
http://localhost.zylk.net:9983
Con estos cambios en el xml ya podremos ejecutar el comando y mandar
a solr la información, y hacer búsquedas sobre el índice.
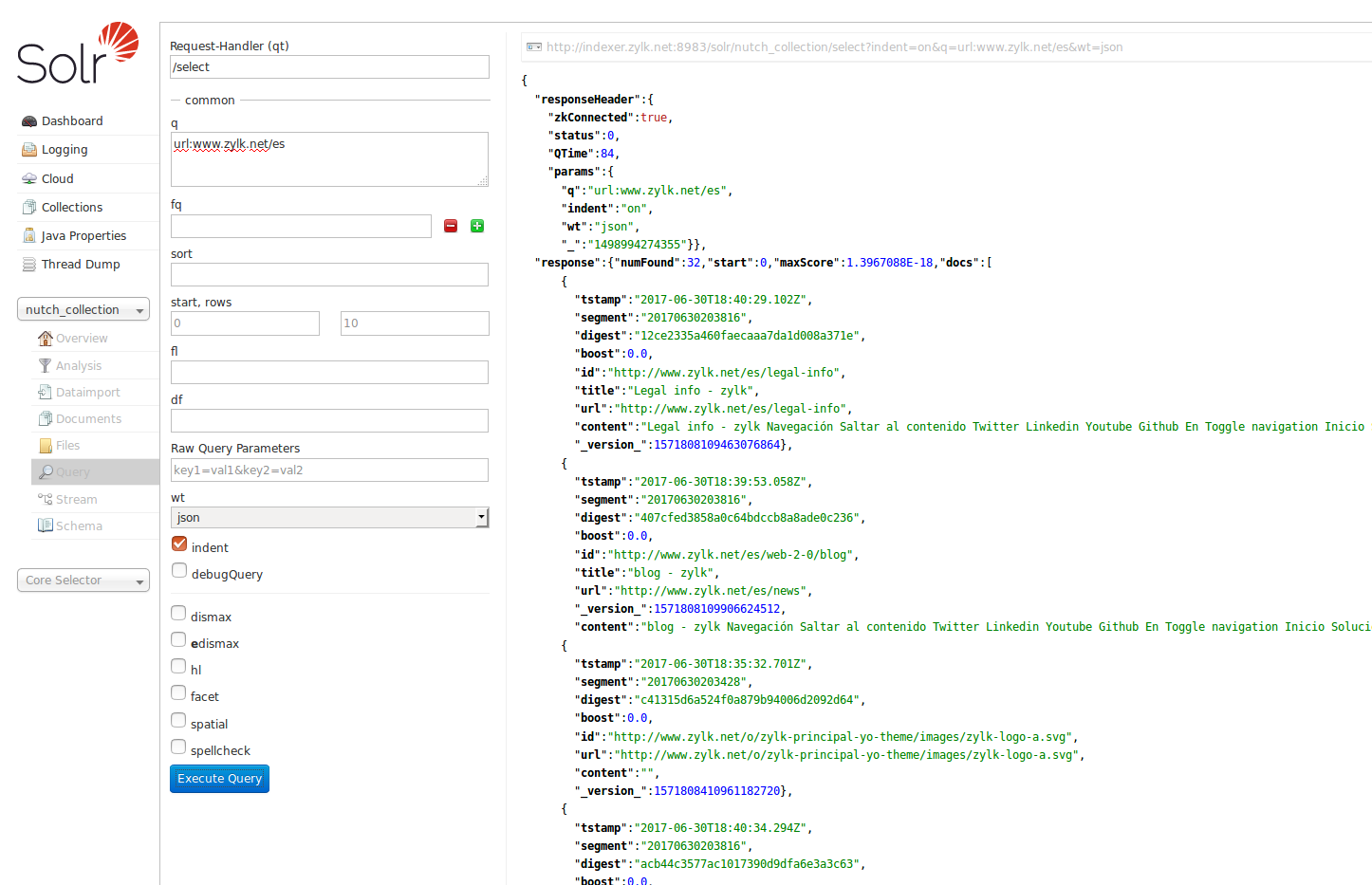
Lo siguiente que estaría bien hacer, es vicular nutch con
HDP para almacenar la información en HBASE, por
ejemplo. Para hacer esto habría que usar la versión 2.x de Nutch que
permite, gracias al proyecto
GORA, usar distintos
sistemas de almacenamiento para el resultado de la recolección.
También habría que usar un cluster de hadoop para poder orquestar el
map-reduce de la recolección usando MapReduce o MapReduce2. Pero esa
prueba para otro día.